Sales forecasting
TBD
Executive Summary
Horizon is a fictitious large telecommunications company operating in California. Customer churn is costing Horizon approximately 60M dollars annually in lost revenue. I developed a logistic regression model that identified at-risk customers with 95% accuracy, enabling targeted retention campaigns that can reduce monthly churn. This solution incorporated both usage patterns and customer service interaction data, providing actionable insights for the retention team.
Business Problem
Horizon was experiencing above-industry-average customer churn rates1, particularly in their fiber optic service segment. Reducing churn represented a significant financial opportunity. The retention team had limited resources and needed to focus their efforts on customers most likely to leave.
Key business questions include:
- Which customers are most likely to churn in the next 60 days?
- What are the primary drivers of customer churn?
- How can retention offers be optimized based on customer profiles?
Data & Methodology
I approached this problem using a combination of customer demographic information, service usage patterns, billing history, and customer service interactions based on representative data from Q3—a typical quarter for operations reflecting typical performance.
Data Sources
- Customer account and services (27 variables including payment, plans and behavioral)
- Customer location (5 variables)
- Customer churn status (satisfaction metrics)
Data for a fictional company for Q3, with numbers taken to be representative of the California business. Source.
Methodology
- Data Preprocessing: Converted 10 categorical features using ordinal encoder.
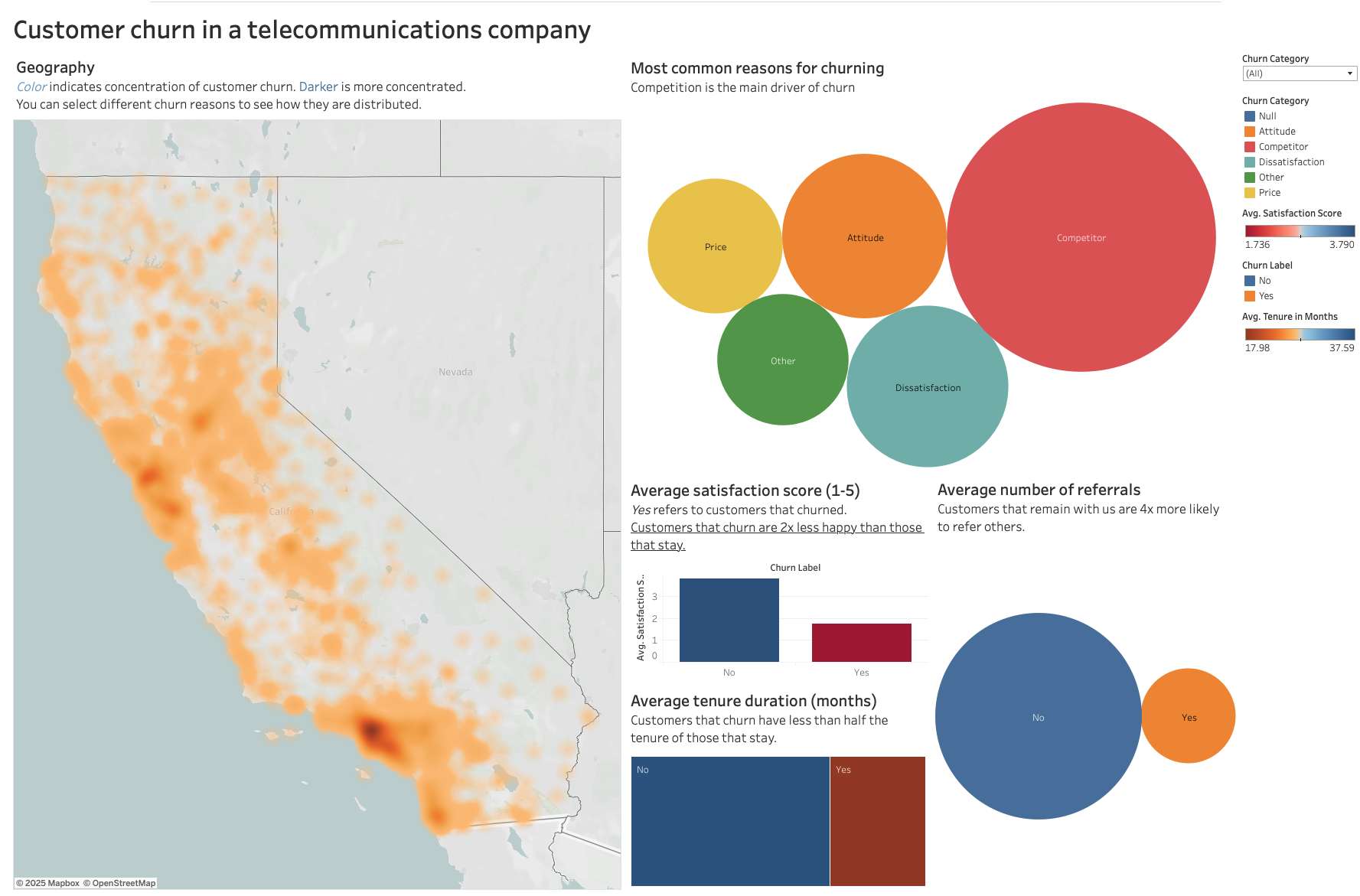
- Exploratory Analysis: Identified where churn is concentrated and strong correlations between number of referrals, type of contract, monthly charge and churn.
- Model Selection: Evaluated logistic regression (baseline), random forest, and gradient boosting models on validation set.
Key Insights & Findings
The analysis revealed several unexpected insights that contradicted initial business assumptions:
-
Monthly charge was the strongest predictor: Customers with larger monthly bills are more likely to churn. This suggests retention strategies targeted at customers with larger bills.
-
Referrals and tenure are the strongest predictor that customer will stay.
-
Customers appreciate the online security package, much more than online backup and streaming service. Customers with online security plans are 70% less likely to churn.
-
New competitor strongly correlated with churn: This is particularly apparent in San Diego.
Solution & Implementation
The final logistic regression model achieved 95% accuracy on validation data.
To make this actionable for the business, I could:
- Develop a weekly automated pipeline to score all customers on churn probability.
- Create customer segments based on churn drivers, enabling targeted retention strategies.
- Build a Tableau dashboard for the retention team to prioritize outreach and recommended retention offers based on customer profiles
- Implement an A/B testing framework to continuously measure retention campaign effectiveness
Technical Resources
- Project Repository
- Interactive Tableau Dashboard
- Jupyter Notebook: Data Exploration
- Jupyter Notebook: Modeling
-
The lost revenue due to customer churn is estimated as follows, based on numbers for large telecom companies. Horizon has $N_{\rm customers}=1$ million customers in California, the annual churning rate is churn$=0.1$ and average revenue per user is ${\rm ARPU} = 12 \times 50 = 600$ dollars. With those numbers, the company is losing $N_{\rm customers} \times {\rm churn}=100,000$ customers per year and $N_{\rm customers} \times {\rm churn} \times {\rm ARPU} = 6 \times 10^7$ dollars in annual revenue. ↩